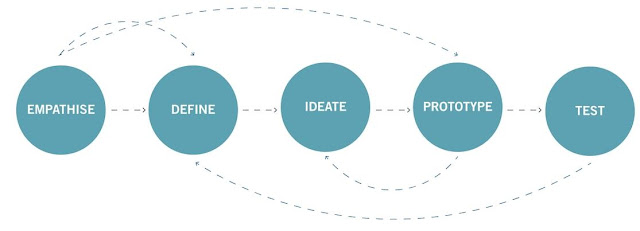
Design Thinking Process
Design Thinking is a design methodology that provides a solution-based approach to solving problems. It is an iterative process in which we seek to understand the user, challenge assumptions, and redefine problems in an attempt to identify alternative strategies and solutions that might not be instantly apparent with our initial level of understanding.
Empathy: Empathize with the intended users of the product by understanding their needs and pain points
Empathy is the foundation. we observe users and their behavior in their context, interact with and interview users, and experience what users experience.Doing so gives you a better understanding of the problem you’re trying to solve
Define: Defining your problem occurs when you unpack and synthesize your empathy findings into compelling insights. The define stage helps you move beyond simple problem statements to a unique design vision that you crafted based on your discoveries. Ask questions that help the group explore various ideas for possible solutions.Think outside the box and look at the problem from different angles.Define the problems as problem statements in a human-centered way.
Ideate: Brainstorm and generate as many relevant, innovative ideas as possible.
During this phase you are searching for a large quantity of ideas and a diversity among the ideas. get creative and come up with ideas and design concepts that address the user’s problems. Unconventional thinking helps teams arrive at innovative solutions. The goal is to come up with as many relevant and innovative ideas as possible.
Prototype: Move forward with the best ideas by creating functional prototypes.
Creating a prototype is to bring ideas to life and select the best possible solution with which to move forward. If you’re attempting to solve multiple problems, implement all of the chosen solutions in a single prototype to ensure they work seamlessly together. Prototypes are ways to demonstrate ideas and to get feedback to build more and more prototypes; they are tools for interaction.
Test: Conduct usability tests to see if the prototype solves the problem.
During the testing stage are often used to redefine the problem and iterate back to an earlier stage

No comments: